Thyroid Care
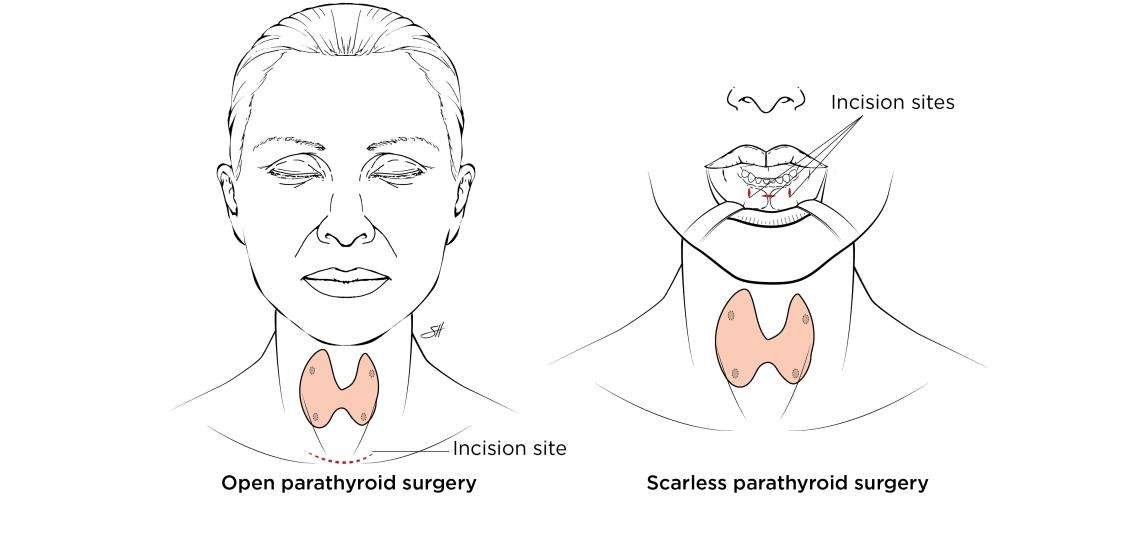
Scarless Endoscopic Thyroid Surgery
Thyroidectomy is a surgical procedure where the doctor removes all or part of the thyroid gland. It is done to treat thyroid problems like thyroid cancer, enlarged thyroid, or overactive thyroid.
Endoscopic thyroid surgery is a special technique that allows the doctor to perform thyroid surgery through small cuts in the skin. It is also called Minimally Invasive Video-Assisted Thyroidectomy. Doctors use this method to avoid leaving a scar on the neck.
During the procedure, the doctor makes very small incisions in the armpit area. A tiny camera is inserted that provides a magnified view of the internal structures on a computer screen. This helps the doctor see the thyroid gland clearly and operate safely and precisely.
The biggest advantage of endoscopic thyroidectomy is that there is no scar on the neck. The small scars in the armpit are hidden under clothes. This is a great benefit for people who are concerned about their appearance. Another advantage is that recovery is faster, usually only 2 days. The magnified view also helps the doctor avoid damaging important nerves and glands during surgery, reducing complications.
In summary, endoscopic thyroidectomy is a minimally invasive surgery that removes the thyroid gland through small cuts in the armpit. It leaves no visible scar on the neck, has a quick recovery time, and reduces the risk of complications.
Microwave Ablation
Microwave ablation is a minimally invasive surgical procedure which helps treat benign thyroid nodules. It involves using heat energy from microwaves to destroy the problematic nodules and reduce their size.
This technique is an alternative to traditional thyroid surgery. It is performed through a small incision, usually around 1 cm, under local anaesthesia. The patient remains awake during the procedure, which typically takes about 30 minutes.
Patients can usually go home within a few hours, unlike with surgery which requires an overnight hospital stay.
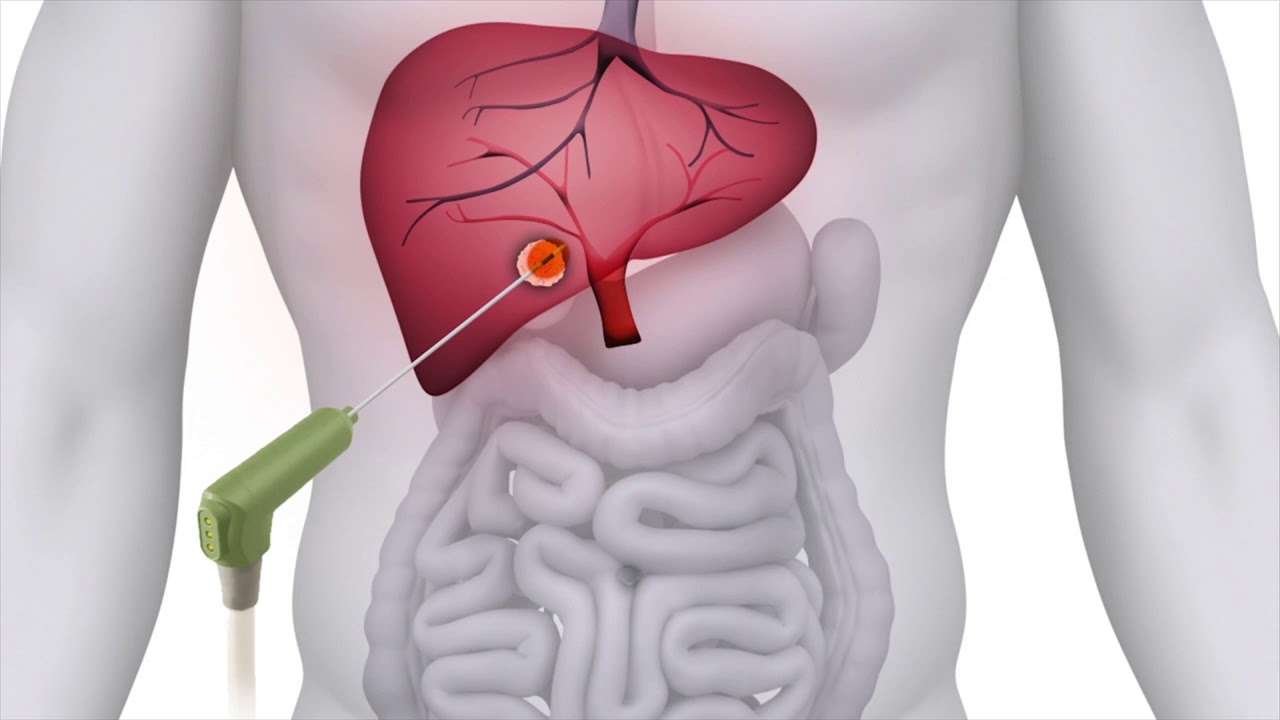
Compared to surgery, microwave ablation has a lower risk of complications such as nerve injury, permanent thyroid hormone replacement, and scarring. However, some risks are still present, though at a lower likelihood, including bleeding, infection, voice changes, skin burns, and nodule regrowth.
Studies have shown that microwave ablation can effectively reduce the size of benign thyroid nodules, with volume reduction rates ranging from 65% to 81% at 6 months to 1 year after the procedure. Patients have also reported improvements in symptoms and cosmetic appearance.
Overall, microwave ablation is a safe and effective alternative to surgery for the treatment of symptomatic benign thyroid nodules. It offers a minimally invasive approach with a quicker recovery time and lower risk of complications compared to traditional thyroidectomy.
Thyroid Cancer Treatments
Thyroid cancer treatments depend on the size of the tumour and whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. Here are the main treatments:
- Radioiodine Therapy : In this treatment, you swallow a pill or liquid containing a higher dose of radioactive iodine than what’s used for diagnostic tests. The radioiodine shrinks and destroys the diseased thyroid gland and cancer cells. This treatment is very safe, as the thyroid gland absorbs most of the radioiodine, and the rest of your body has minimal radiation exposure.
- Chemotherapy : Chemotherapy uses intravenous or oral drugs to kill cancer cells and stop their growth. Very few people with thyroid cancer will need chemotherapy.
- Hormone Therapy : Hormone therapy blocks the release of hormones that can cause cancer to spread or come back.
These treatments are suited to each patient’s specific needs based on the size and spread of the thyroid cancer.
Advanced Thyroid Cancer Treatment
Thyroid cancer can sometimes become more serious or come back after treatment. When it returns, it usually appears in the lymph nodes in the neck. Many of these tumours grow slowly, and some don’t grow at all.
- Surgery : Surgery is one of the most common treatments for the advanced stages of thyroid cancer. The surgeon may remove part of the thyroid gland or the entire gland. They will also remove any nearby lymph nodes where cancer cells have spread.
- Radiation Therapy : Radiation therapy uses strong beams of energy to kill cancer cells and stop their growth. External radiation therapy uses a machine to deliver the beams directly to the tumour. Internal radiation therapy, on the other hand, involves placing radioactive seeds in or around the tumour.
- Chemoradiation : This is a treatment that combines chemotherapy with radiation. It can be given as proton therapy or IMRT.